Understanding AC Power Supply: The Backbone of Modern Electronics Explained Simply
In the realm of modern electronics, the AC power supply serves as a fundamental component that powers a vast array of devices, from household appliances to industrial equipment. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global power supply market is projected to reach $30 billion by 2025, reflecting an increasing demand for reliable and efficient power solutions. This growth is largely driven by advancements in technology and the rising adoption of electronic devices across various sectors.
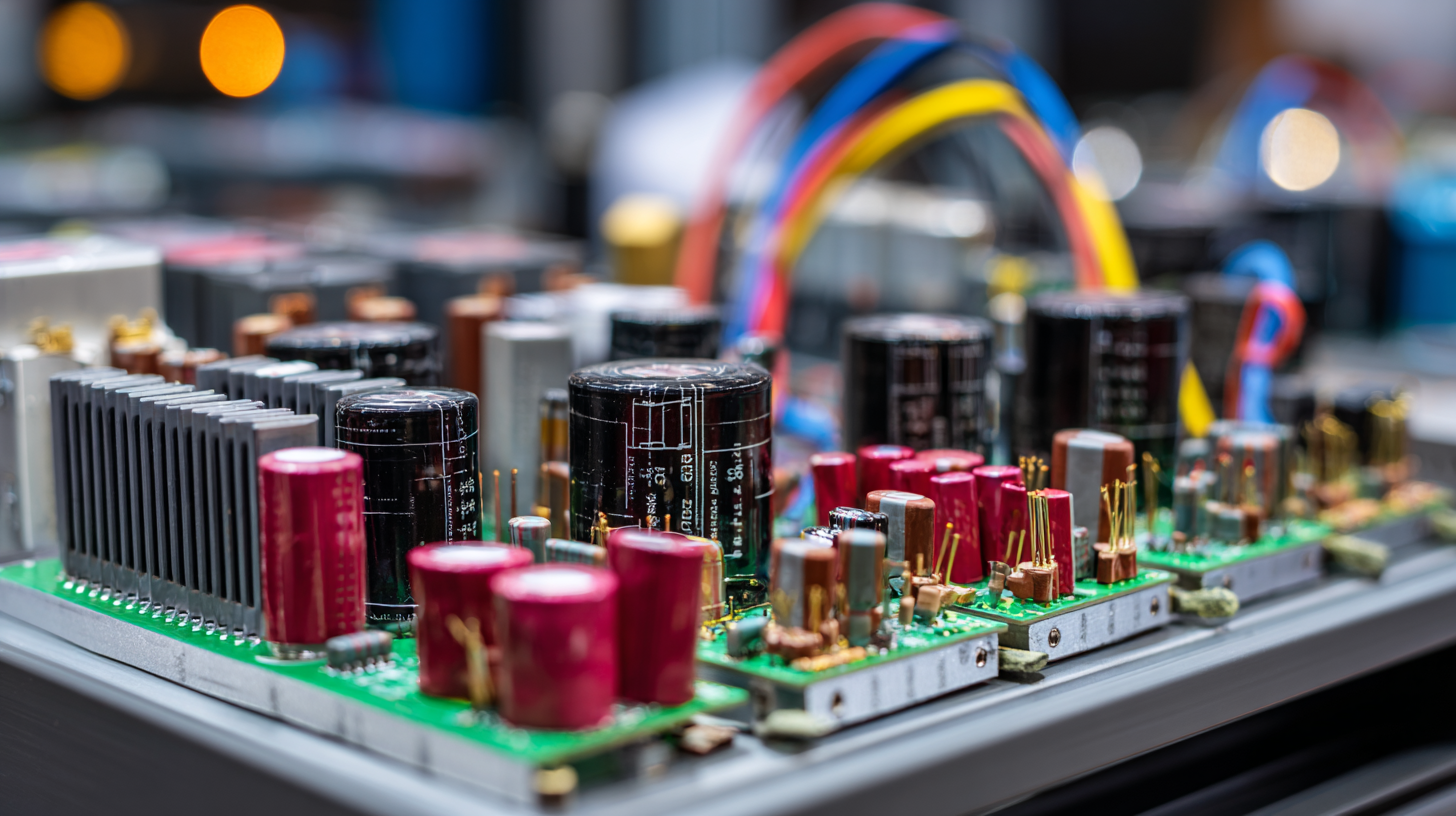
AC power supplies, in particular, are critical for converting alternating current from the grid into a usable form for sensitive electronic circuits, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Understanding the principles behind AC power supply not only empowers consumers to make informed choices but also helps engineers to innovate within the evolving landscape of electronic design. As we delve into the intricacies of AC power supply, we uncover its vital role in supporting the seamless operation of modern technology.
What is AC Power Supply and Why is it Essential?
AC power supply refers to the system that provides alternating current (AC) electricity to power various devices and appliances. Unlike direct current (DC), where the flow of electricity is constant, AC power reverses direction periodically, making it more efficient for long-distance transmission. This reversibility allows for the utilization of transformers that can step up or step down voltage levels depending on the requirements of different applications. Consequently, the AC power supply is a crucial element in ensuring that homes, industries, and commercial establishments receive the electricity needed to operate safely and effectively.
The essential nature of AC power supply is underscored by its widespread use in modern electronics. From household items such as refrigerators and televisions to industrial machinery and infrastructure, AC power is integral to our daily lives. It supports not only the basic operations of devices but also enables advanced technologies that rely on stable and reliable electricity. Without AC power supply, the function and development of modern electronics would be severely impeded, highlighting its role as the backbone of contemporary electrical systems.
Understanding AC Power Supply: Essential Insights
Key Components of an AC Power Supply Explained
An AC power supply is essential in modern electronics, serving as the backbone that powers various devices and systems. Key components of an AC power supply include transformers, which modulate voltage levels, and rectifiers, which convert AC to DC power. Voltage regulators ensure stable voltage output despite fluctuations in input power, thereby protecting sensitive electronic components from damage. Additionally, capacitors are employed to smooth out voltage variations, allowing for consistent energy delivery.
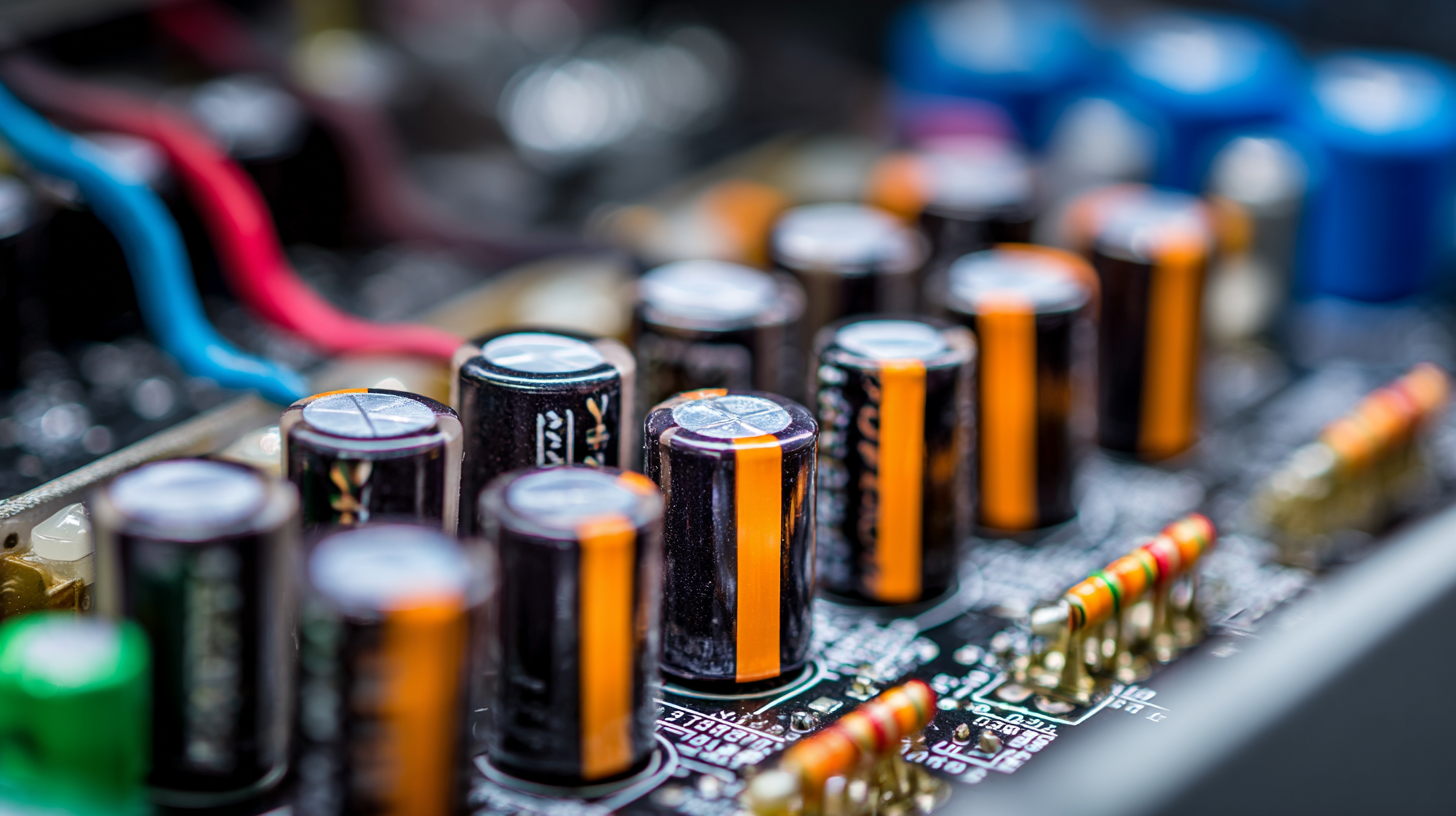
The market for power supply technologies, particularly switching mode power supplies (SMPS), is experiencing significant growth. This increase is driven by the demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries, leading to advancements in technology. SMPS offer improved efficiency through rapid switching and are available in different configurations, including linear and switching types. Understanding these components and market trends is crucial for stakeholders in the electronics industry, facilitating smarter design choices and investments in energy-efficient systems. By effectively managing power supply systems, the industry can optimize performance while reducing environmental impact.
How AC Power is Generated and Delivered to Homes
AC power supply is essential to modern life, allowing for the operation of various devices in our homes. The generation of alternating current (AC) typically begins at power plants, where massive generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), about 63% of electricity in the United States is generated from fossil fuels, while renewable sources like wind and solar contribute approximately 20%. This diverse energy mix ensures a steady and reliable supply of electricity for households.
Once generated, AC power travels through an extensive network of transmission and distribution lines. High voltage transmission lines help minimize energy loss over long distances, as detailed in the report by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). After reaching substations, the voltage is lowered for safe distribution to homes. The entire system operates at a frequency of 60 Hz in North America, allowing for compatibility with the majority of household appliances. This intricate process underscores the importance of AC power supply in our daily lives, powering everything from refrigerators to entertainment systems.
Understanding Voltage, Current, and Frequency in AC Power
Alternating current (AC) power supply is a critical component in modern electronics, and understanding its fundamental aspects—voltage, current, and frequency—is essential for grasping how devices function.
Voltage, the electrical potential difference, is crucial as it drives the flow of electric current through circuits. In most residential and commercial settings, AC voltage typically oscillates between 120V and 240V, adapting to the needs of various appliances and ensuring safe and efficient power delivery.
Current, which represents the flow of electric charge, varies based on the load connected to the power source. In AC systems, this flow alternates direction, meaning both the voltage and current can change their magnitude and direction over time. This characteristic allows for efficient transmission over long distances and helps in reducing energy loss.
Furthermore, the frequency of AC power, usually measured in hertz (Hz), indicates how often the current changes direction each second. In many countries, the standard frequency is either 50Hz or 60Hz, impacting how electronic devices are designed and function. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone engaged in the field of electronics, as they form the foundation for functioning electrical systems.
Common Applications of AC Power in Modern Electronics
AC power supply plays a crucial role in modern electronics, serving as the foundation for numerous applications across various industries. One of the most common uses of AC power is in household and commercial appliances, where it is the primary source of energy. Devices such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines rely on AC power to function efficiently, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy and thermal energy to ensure optimal performance.
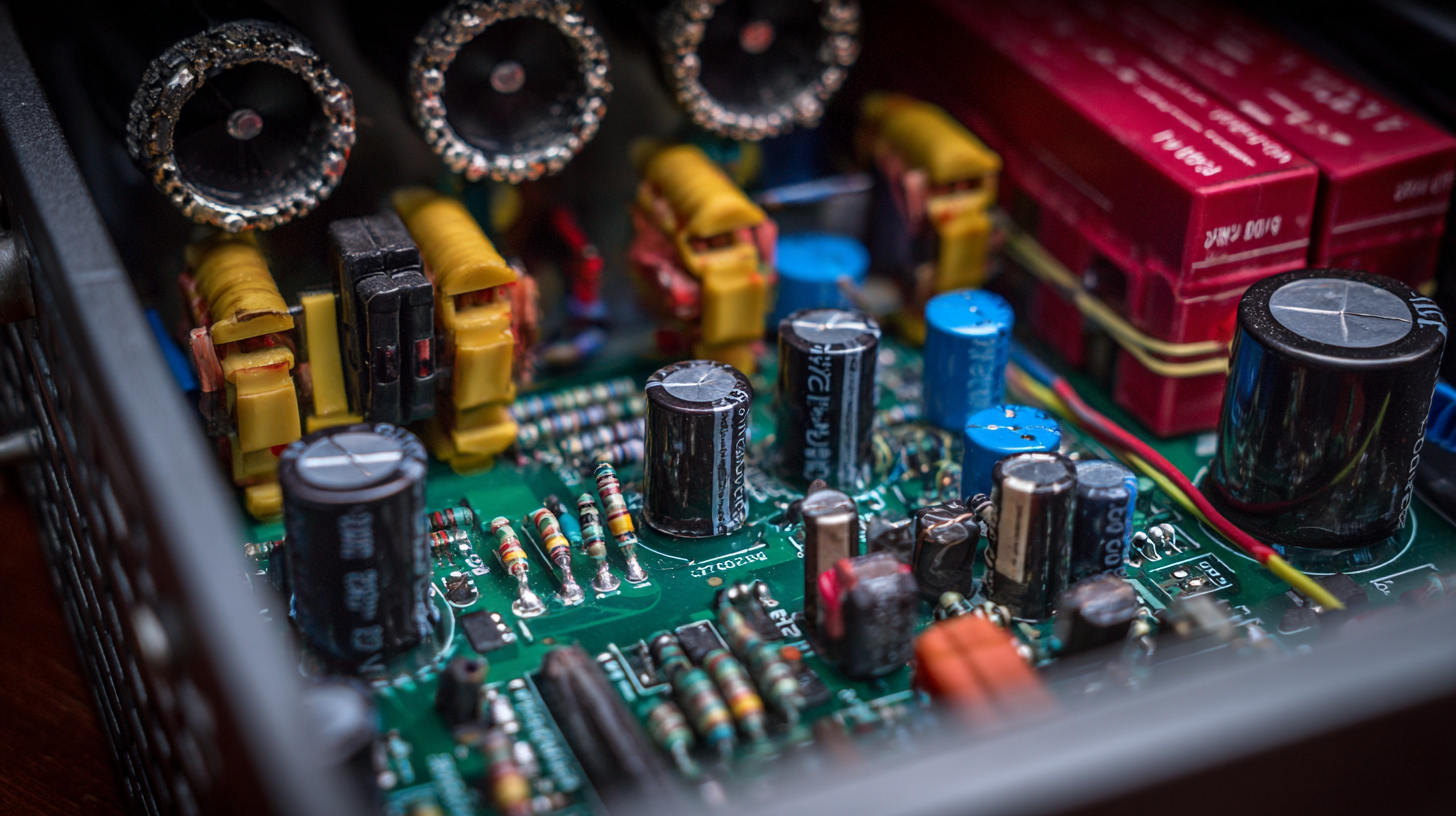
Additionally, AC power is vital in telecommunications and data centers where uninterrupted power supply systems are essential. These facilities utilize AC power to maintain the operation of servers, communication equipment, and other critical infrastructure. Moreover, AC power is fundamental in powering electric motors for industrial applications, enabling automation and enhancing productivity. As technology continues to evolve, the efficiency and reliability of AC power systems remain key to the advancement of modern electronics, driving innovation across various sectors.
Related Posts
-
Unlocking Efficiency: How Buck Converters Achieve Over 95% Power Conversion in Modern Electronics
-

5 Essential Tips to Optimize Your UPS Electrical Systems for Maximum Efficiency
-

Digital Solutions Tips for Optimizing Your DC DC Converter Performance
-
How to Select the Best Buck Converter for Efficient Power Management in Your Application
-
Understanding the Importance of DC to AC Converters in Modern Power Systems
-

How to Choose the Right ATX Power Supply for Your PC Build
At Premium PSU, we are specialists in designing and manufacturing power conversion systems for the industrial market. Our product range includes high reliability power supplies from 50W to 72kW.
PREMIUM PSU
C/ Dolors Aleu, 19-21, 2nd Floor
08908 – Hospitalet de Llobregat
Barcelona-SPAIN
t.+34 93 223 26 85


